42 how often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered?
Porifera and Cnidaria Flashcards | Quizlet Nematocysts are a specialized cell in the tentacles of a cnidarian containing a barbed or venomous coiled thread that can be projected in self-defense or to catch prey. ... How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered? Once. Draw and label the stages of a Nematocyst discharge. ... Fossils are most often found in a. soil. b ... 29 where are the 2 main locations of nematocysts a - Course Hero When the small trigger on the cell is stimulated, a rapid increase in osmotic pressure within the cnidocyte causes the nematocyst to discharge violently, exploding out of the cell and releasing a long, hollow, thread like filament, driving its barbs and poison into the flesh of its victim. 31. How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be ...
How often can the mechanism in the nematocysts be triggered ... - Answers Cnidarians use their nematocysts to capture prey and as a defense mechanism against predators. How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered? Only once.

How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered?
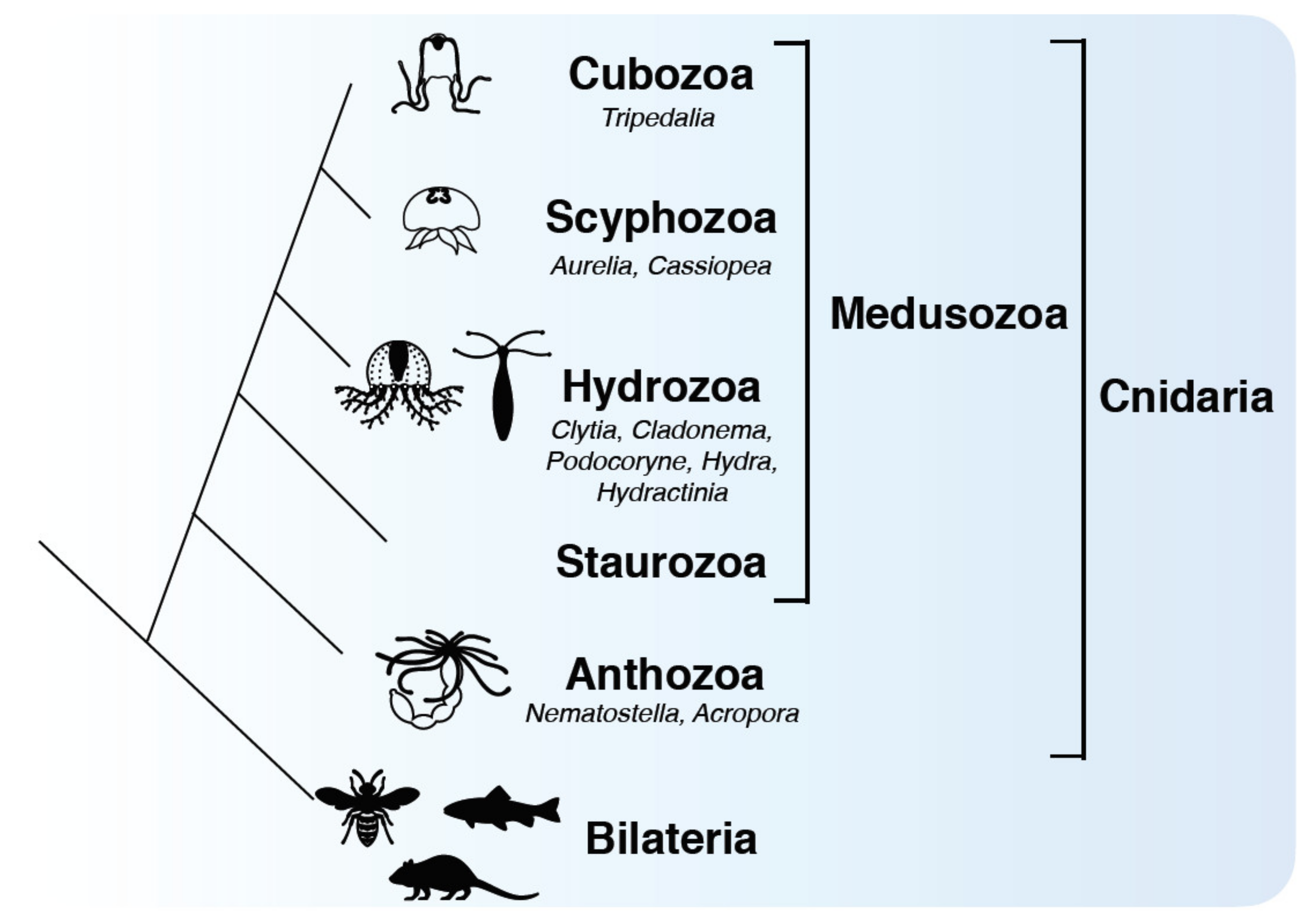
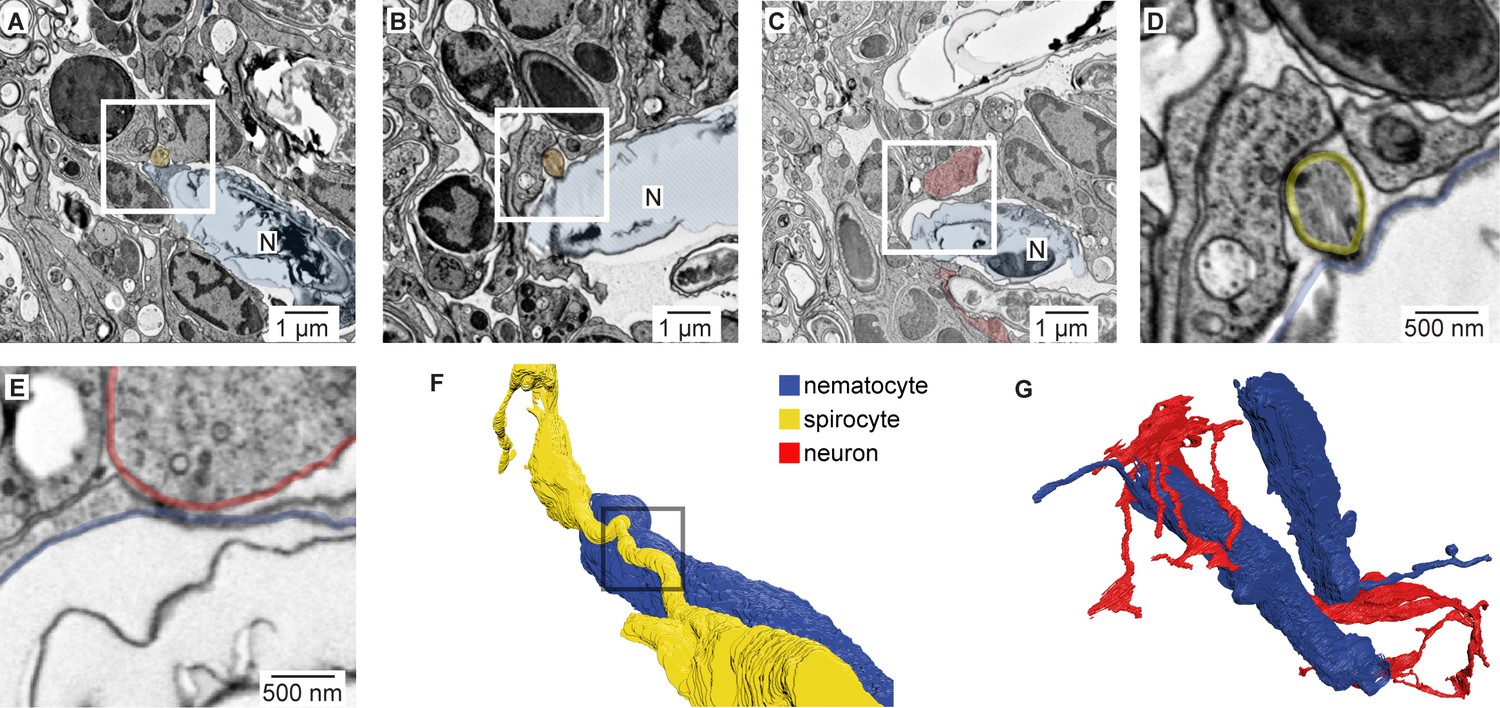
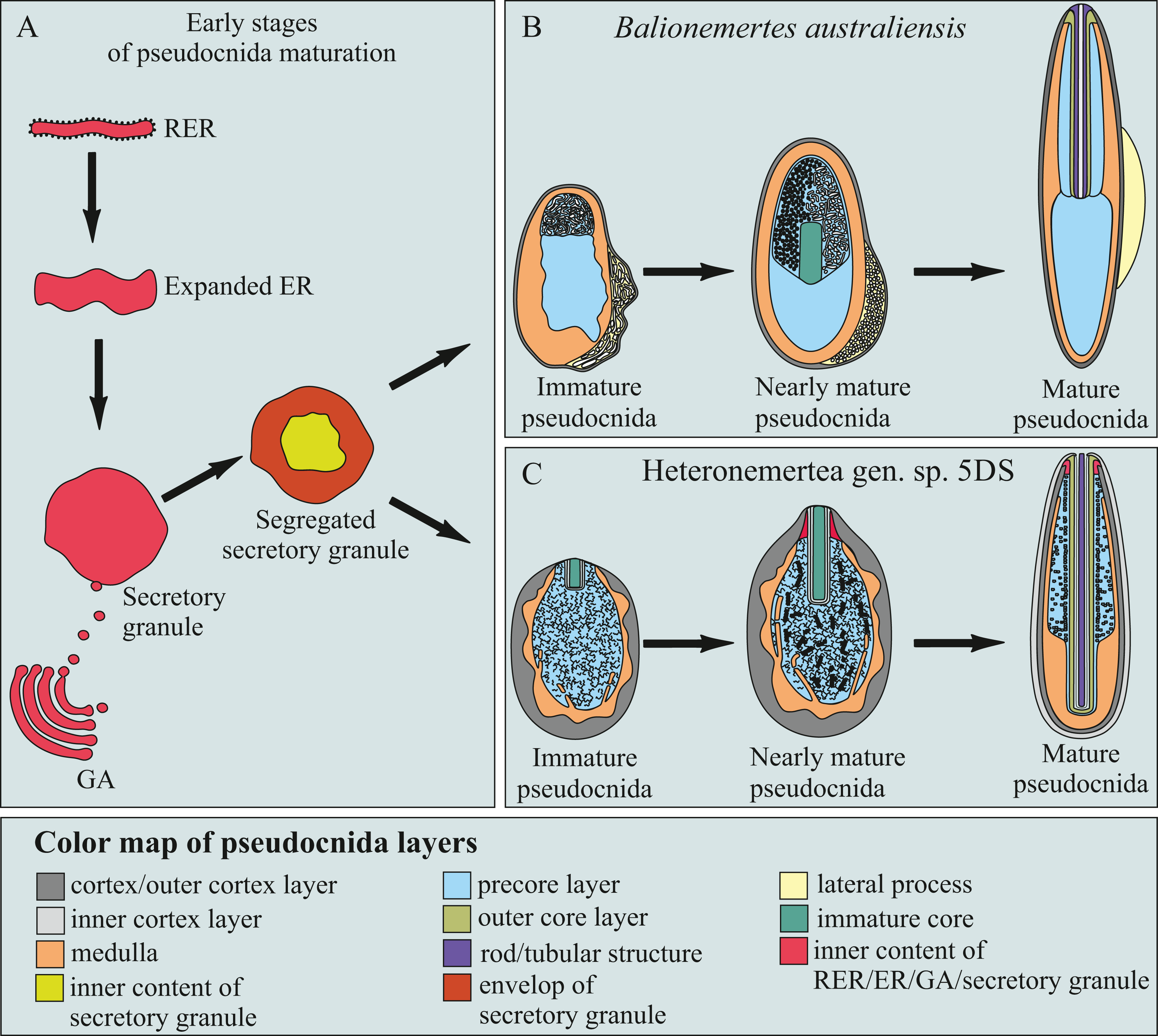
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › CnidariaCnidaria - Wikipedia Cnidaria (/ n ɪ ˈ d ɛər i ə, n aɪ-/) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Proteome of Hydra Nematocyst - PMC The existence of nematocyst-like organelles in dinoflagellates and other protozoans argues for an evolutionary origin of nematocysts predating multicellularity (Fig. 6). The nematocyst proteome can therefore shed light into the primordial state of the ECM to which the nematocyst's biomechanical requirements probably contributed. Formation and discharge of nematocysts is controlled by a proton ... Cnidaria catch and kill their prey by means of nematocysts. A nematocyst consists of a capsule containing a coiled tubule. On triggering, the cyst extrudes this tubule in an extremely rapid manner. The mechanisms and driving forces of discharge are still unknown. We found nematocysts of various cnidarians to be acidic inside and propose that the pH difference between cyst matrix and cytoplasm ...
How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered?. Inside the jellyfish's sting: Exploring the micro ... - ScienceDaily "The earliest phase of the firing of the nematocyst is extremely fast and hard to capture in detail," said Karabulut. advertisement As is often the case in fundamental biological research, the ... Sequestration of nematocysts by divergent cnidarian predators ... predators. Nematocyst sequestration has evolved multiple times, having been documented in Ctenophora, Acoelomorpha, Platyhelminthes, and Mollusca. For each of these phyla, we review the phylogenetic distribution, mechanisms, and possible functions of nematocyst sequestration. We estimate that nematocyst sequestration has evolved 9-17 times across these When do Nematocysts discharge? - Answers Nematocyst discharge is triggered by an immediate approach or a foreign stimulus. When the cell is discharged, a brand new nematocyst is created as the system in each cell can only be activated... Box jellyfish - Wikipedia Box jellyfish (class Cubozoa) are cnidarian invertebrates distinguished by their box-like (i.e. cube-shaped) body. Some species of box jellyfish produce potent venom delivered by contact with their tentacles. Stings from some species, including Chironex fleckeri, Carukia barnesi, Malo kingi, and a few others, are extremely painful and often fatal to humans.
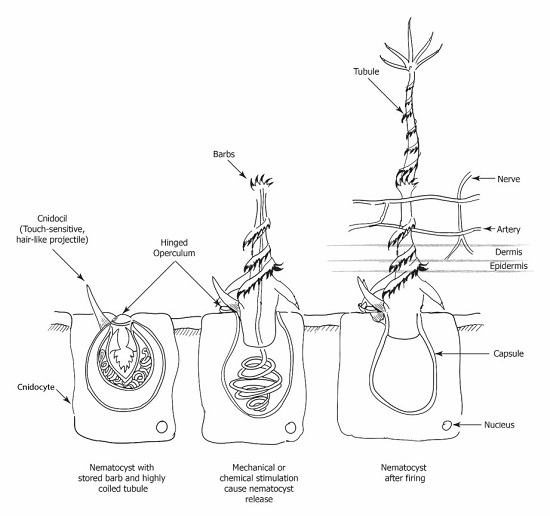
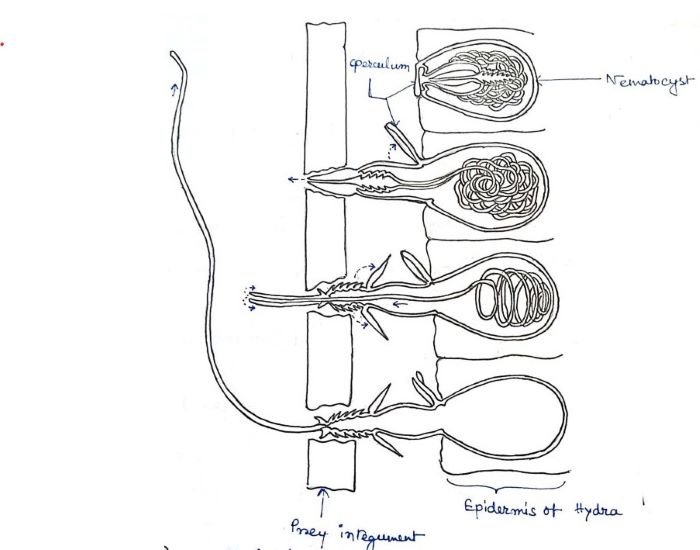
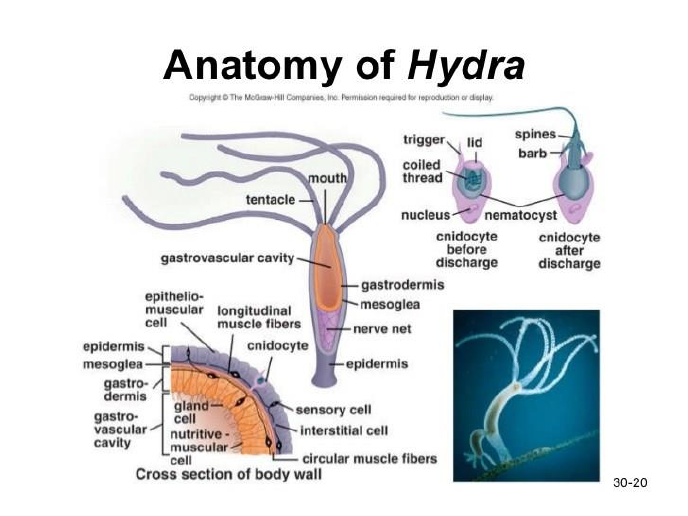
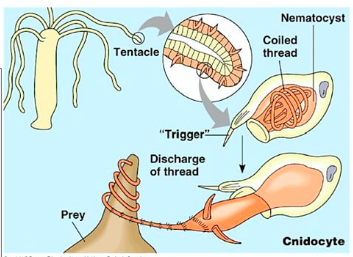
Nematocysts - The Stinging Cells | Zoology for IAS, IFoS and other ... The bladder is covered on the top by a lid or operculum, near which lies a hair-like process, the cnidocil that acts like a trigger for the discharge of the thread tube. Cytoplasm of cnidoblast may contain contractile muscle fibrils and a restraining thread at the base, called lasso, which prevents the nematocyst from being thrown out of cell ... Nematocyst - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The sting is often caused by nematocysts located on jellyfish. These nematocysts release a toxin that caused the symptoms in our patient. The unexploded nematocysts can be inactivated with topical application for 30 minutes of 3% acetic acid, a slurry of baking soda, or meat tenderizer (papain). Papain should not be left on for more than 15 ... › animals › dangerous-jellyfis5 Most Dangerous Jellyfish in the World | Planet Deadly Nov 25, 2013 · When these stinger cells are triggered the internal pressure builds up to a massive 2,000 psi (136 atmospheres) whereupon it bursts, firing out a toxin harpoon. This is one of the fastest movements in nature and quicker than a bullet [1] Cnidarian internal stinging mechanism | ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Sequestration of nematocysts by divergent cnidarian predators ... For each of these phyla, we review the phylogenetic distribution, mechanisms, and possible functions of nematocyst sequestration. We estimate that nematocyst sequestration has evolved 9-17 times ...
Chapter 1: Envenomations - Divers Alert Network This skin rash can take several days to resolve. Often, the skin reaction will subside in a day or two, but it may likely reappear several days or weeks after the initial rash disappeared. ... Cnidarian tentacles are like nematocyst-coated spaghetti, so rubbing the area or allowing the tentacles to roll over the skin will exponentially increase ... en.wikipedia.org › wiki › JellyfishJellyfish - Wikipedia Names. The name jellyfish, in use since 1796, has traditionally been applied to medusae and all similar animals including the comb jellies (ctenophores, another phylum). The term jellies or sea jellies is more recent, having been introduced by public aquaria in an effort to avoid use of the word "fish" with its modern connotation of an animal with a backbone, though shellfish, cuttlefish and ... Learn About Nematocyst | Chegg.com The main function of nematocysts is to produce a harpoon-like thread to inject into their enemy or prey. Their mechanism of action in killing their enemy is by injecting a neurotoxin into them. The toxin is produced by ectodermal gland cells of surrounding nematocysts. Their sting is very painful and can lead to paralysis or death of an organism. The Nematocyst: a molecular map of the Cnidarian stinging organelle Inside each nematocyst is a coiled and eversible tubule, which can be discharged to deliver a venomous sting (Beckmann & Özbek, 2012). Venom is a cocktail of toxic compounds, stored inside the ...
Chapter 7 Flashcards | Quizlet When a cnidocyte is triggered it fires a stinging cell called a nematocysts. When stimulated to discharge the permeability of the nematocyst changes and the internal osmotic pressure causes water to rush into the capsule. The operculum opens and rapidily increasing hydrostatic pressure within the capsule force the thread outward, the thread ...
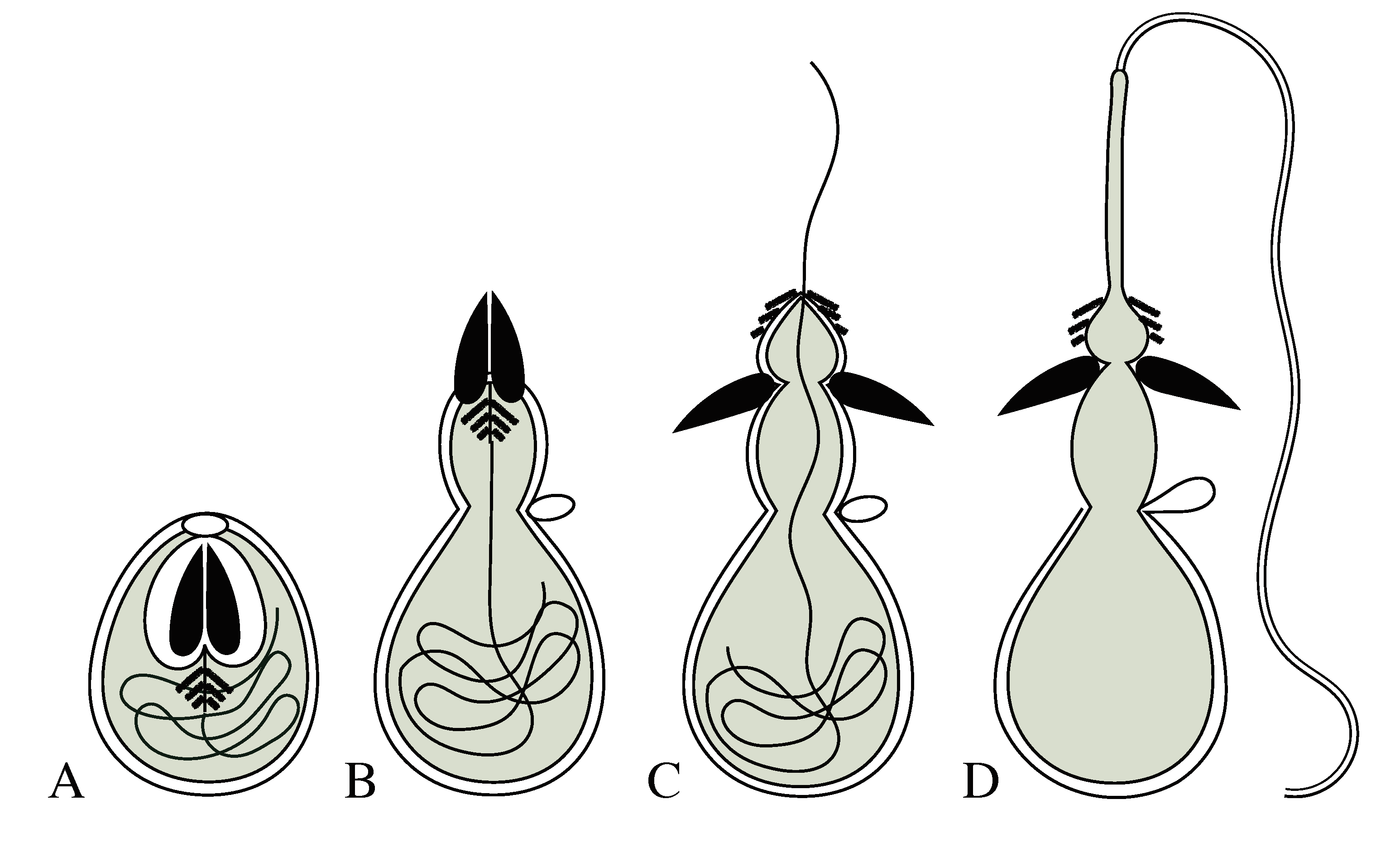
PDF Cnidarians: Jellyfish, coral, sea anemones & hydra What causes a nematocyst to discharge? 14. How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered? 15. Draw and label the stages of a nematocyst discharge. Name: _____ Date: _____ Period: _____ Human Uses: 16. How do humans use cnidarians? Status & Threats: ...
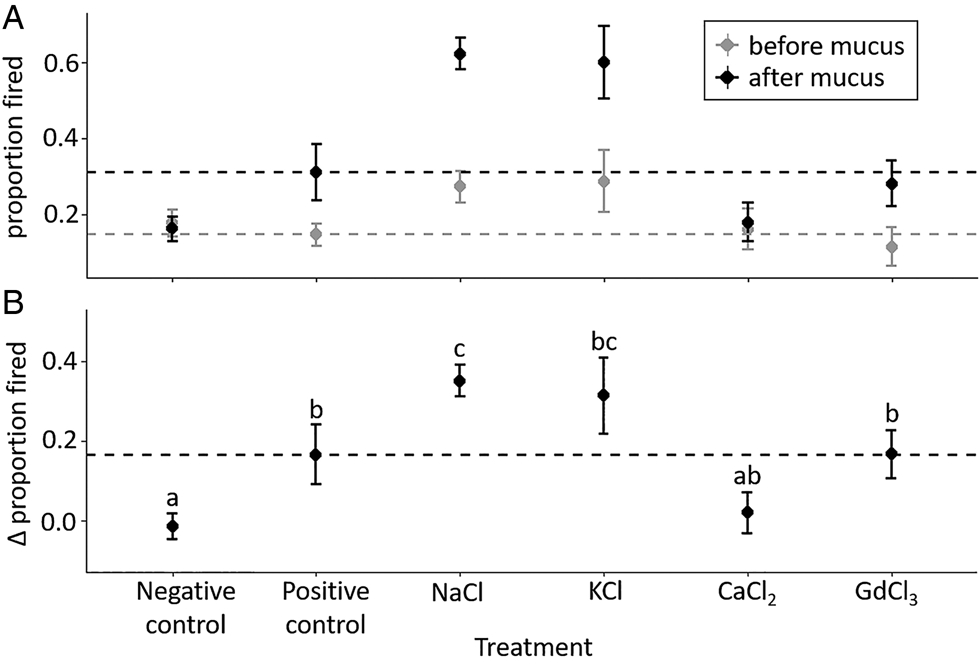
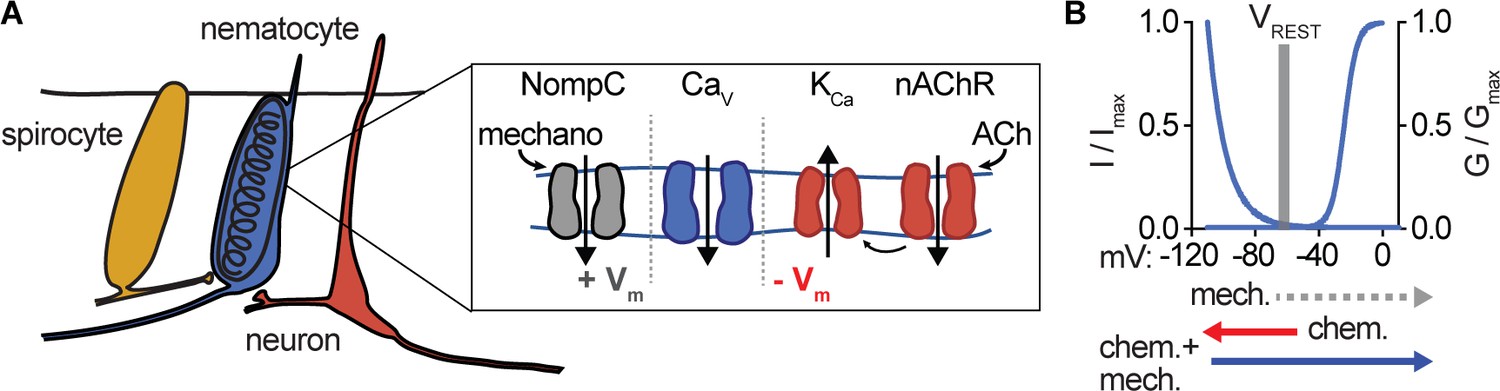
PDF A Molecular Trigger for Sea Anemone Stinging cues synergistically trigger nematocytes to rapidly fire a venom-covered barb (nematocyst) through a previously unknown mechanism. Here, I show that nematocytes from Nematostella vectensis use a specialized voltage-gated calcium channel (nCa V) to distinguish salient sensory cues and control the explosive discharge response.
Nematocyst Stingers Accelerate Fast — Biological Strategy — AskNature The Strategy. The cells (cnidocysts) produce one large organelle called a nematocyst. The cell forms a layered. polymer. matrix around the nematocyst that keeps it strong and promotes the generation of 150 bar of pressure within the organelle at maturation. The "lid" of the capsule (operculum) associates with the cell membrane facing out.
Inside the jellyfish's sting: Exploring the micro-architecture of a ... "The earliest phase of the firing of the nematocyst is extremely fast and hard to capture in detail," said Karabulut. As is often the case in fundamental biological research, the initial discovery ...
nematocyst | biology | Britannica nematocyst, minute, elongated, or spherical capsule produced exclusively by members of the phylum Cnidaria (e.g., jellyfish, corals, sea anemones). Several such capsules occur on the body surface. Each is produced by a special cell called a cnidoblast and contains a coiled, hollow, usually barbed thread, which quickly turns outward (i.e., is everted) from the capsule upon proper stimulation.
A fast recoiling silk-like elastomer facilitates nanosecond nematocyst ... Background The discharge of the Cnidarian stinging organelle, the nematocyst, is one of the fastest processes in biology and involves volume changes of the highly pressurised (150 bar) capsule of up to 50%. Hitherto, the molecular basis for the unusual biomechanical properties of nematocysts has been elusive, as their structure was mainly defined as a stress-resistant collagenous matrix ...
PDF Cnidarians: Jellyfish, coral, hydra & sea anemones Cnidarian Basics 31.What causes a Nematocyst to discharge? 32.How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered? 33. Draw and label the stages of a Nematocyst discharge. Human Uses: 34.How do humans use cnidarians? Status & Threats: 35. How do humans place the survival of cnidarians in danger?
PDF Sponges & Cnidarian Webquest Worksheet - Science by Shaw In the ocean, live sponges can be found in an infinite variety of colors and shapes. Most of them are relatively small, but some varieties can grow to over 6 feet in diameter. ... 31.What causes a Nematocyst to discharge? 32.How often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered? 33. Draw and label the stages of a Nematocyst discharge.
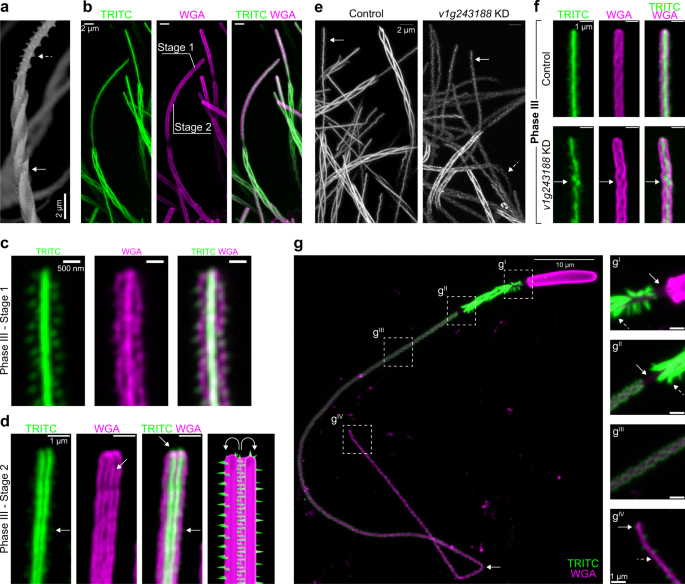
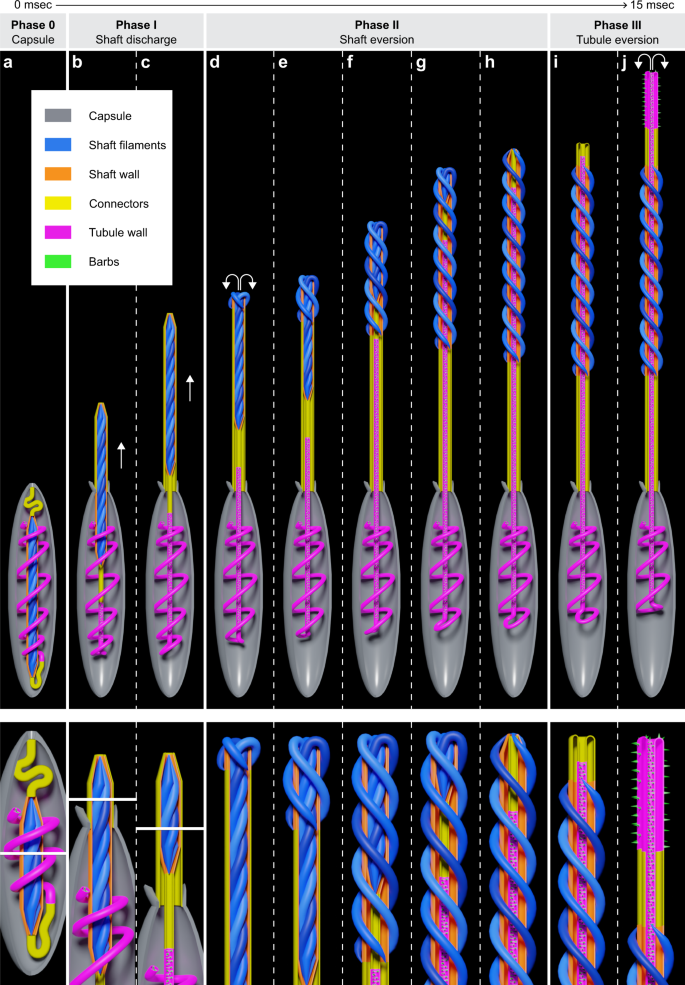
Mechanism of Nematocyst Discharge and Its Cellular Control Abstract. Cnidarians possess unique intracellular organelles, cnidae, which discharge by evaginating their tubular contents following certain appropriate stimuli. Every cnida consists of a capsule, a tubule or shaft, or combination of the two, and intracapsular fluid and is contained in a cell called a cnidocyte.
Functions of Nematocysts in Cnidarians - Study Nature When the nematocyst is triggered, it will shoot out a coiled thread of protein. ... These threads are extremely thin and can be as long as 15 times the length of the nematocyst itself. The threads can open pores in prey organisms, which then allows toxins to flow into them. ... The nematocysts on the tentacles are often larger than those found ...
Sequestration of nematocysts by divergent cnidarian predators ... Adaptations to avoid predation are extremely common and diverse among animals. Such adaptations can take a variety of forms, including behavioral, physical, or chemical defenses, and can be generated through diverse mechanisms (Adler & Harvell 1990; Pawlik 1993; Cresswell 1994; Stachowicz & Lindquist 2000).Although defenses are often produced endogenously, being entirely encoded by the genome ...
Formation and discharge of nematocysts is controlled by a proton ... Cnidaria catch and kill their prey by means of nematocysts. A nematocyst consists of a capsule containing a coiled tubule. On triggering, the cyst extrudes this tubule in an extremely rapid manner. The mechanisms and driving forces of discharge are still unknown. We found nematocysts of various cnidarians to be acidic inside and propose that the pH difference between cyst matrix and cytoplasm ...
Proteome of Hydra Nematocyst - PMC The existence of nematocyst-like organelles in dinoflagellates and other protozoans argues for an evolutionary origin of nematocysts predating multicellularity (Fig. 6). The nematocyst proteome can therefore shed light into the primordial state of the ECM to which the nematocyst's biomechanical requirements probably contributed.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › CnidariaCnidaria - Wikipedia Cnidaria (/ n ɪ ˈ d ɛər i ə, n aɪ-/) is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter.
























Post a Comment for "42 how often can the mechanism in the nematocyst be triggered?"