43 nitrogen cycle label
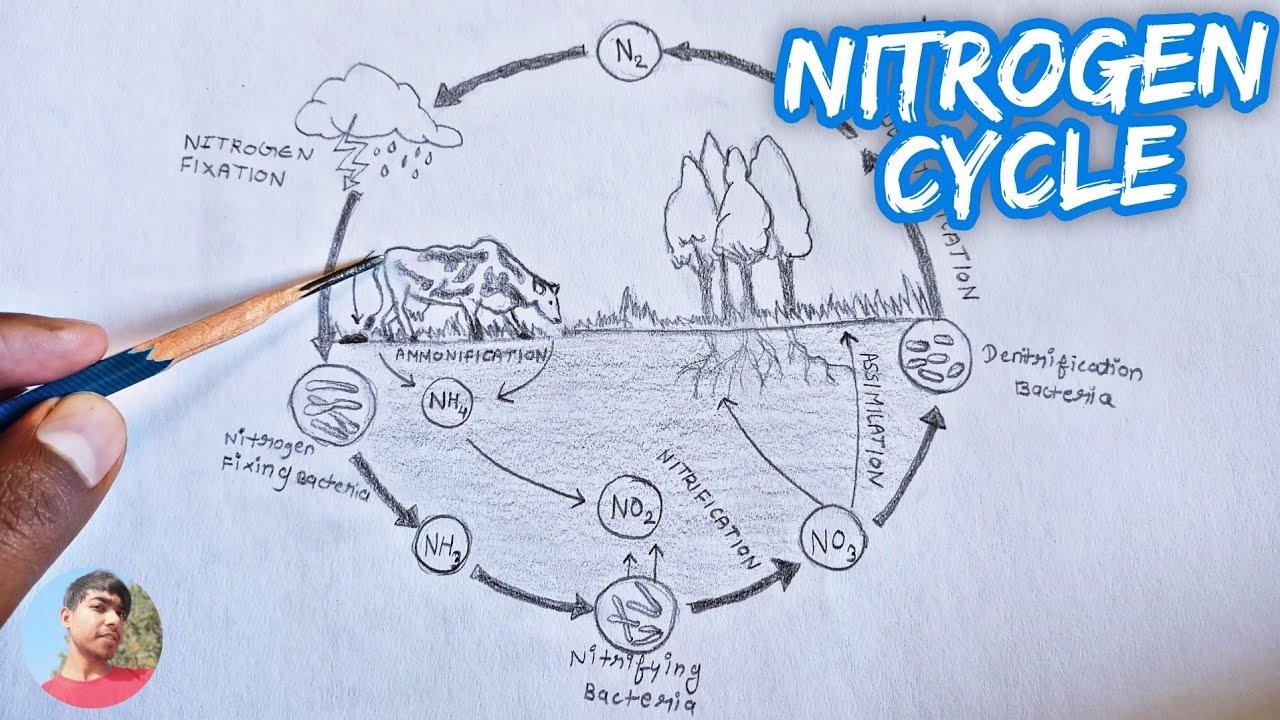
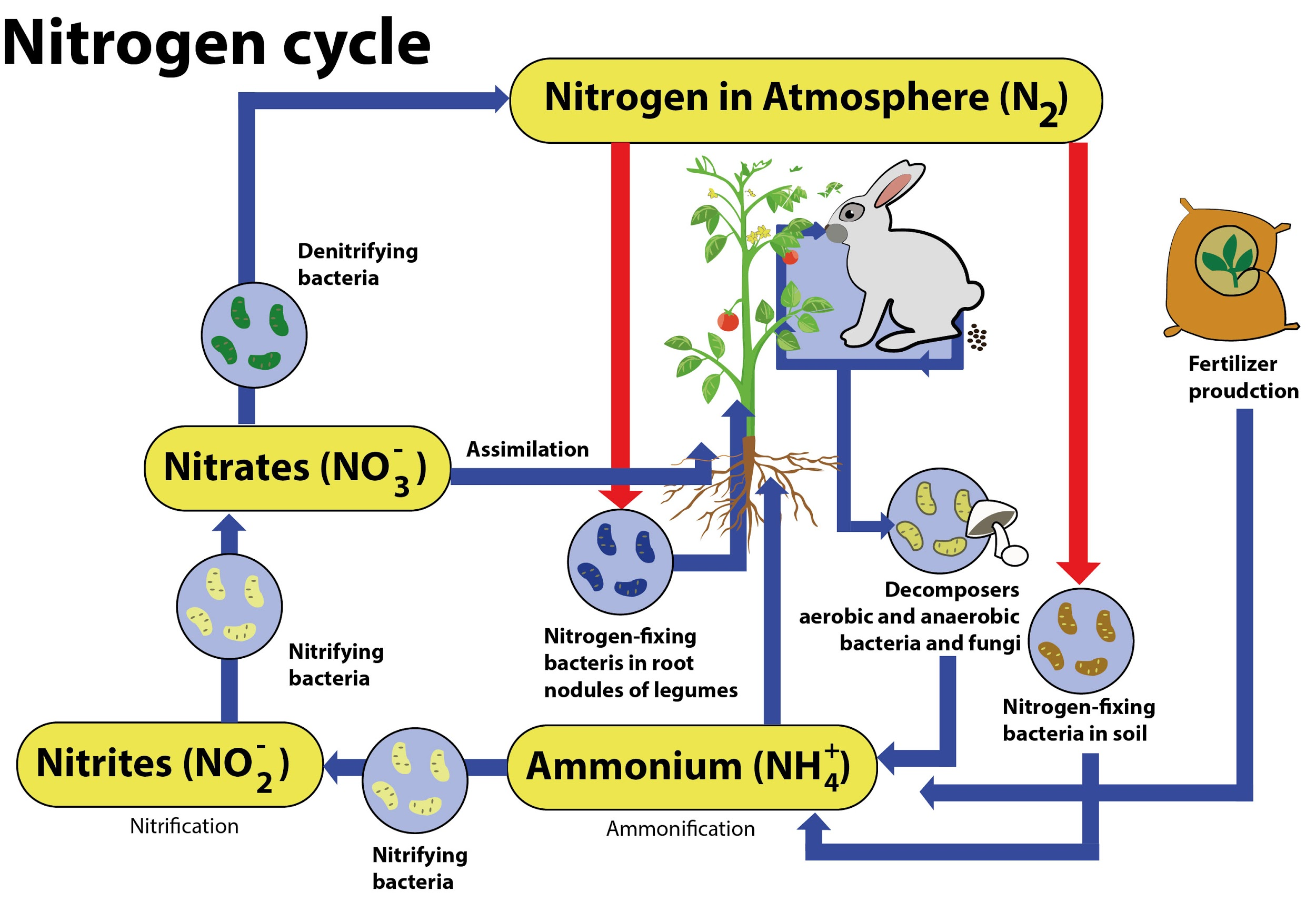
The Nitrogen Cycle: Processes, Players, and Human Impact The process of converting N 2 into biologically available nitrogen is called nitrogen fixation. N 2 gas is a very stable compound due to the strength of the triple bond between the nitrogen... Nitrogen Cycle | BioNinja The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle whereby nitrogen is converted into various chemical forms. Whilst ~78% of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen (N2), this gas is inert and unable to be used by plants and animals. Chemoautrophic bacteria can convert this nitrogen gas into compounds that can be assimilated by plants and animals.
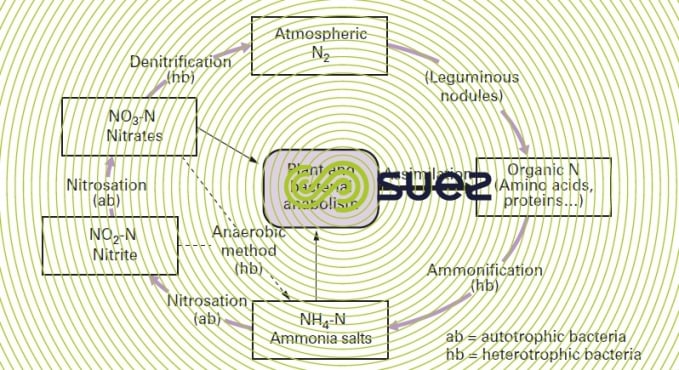
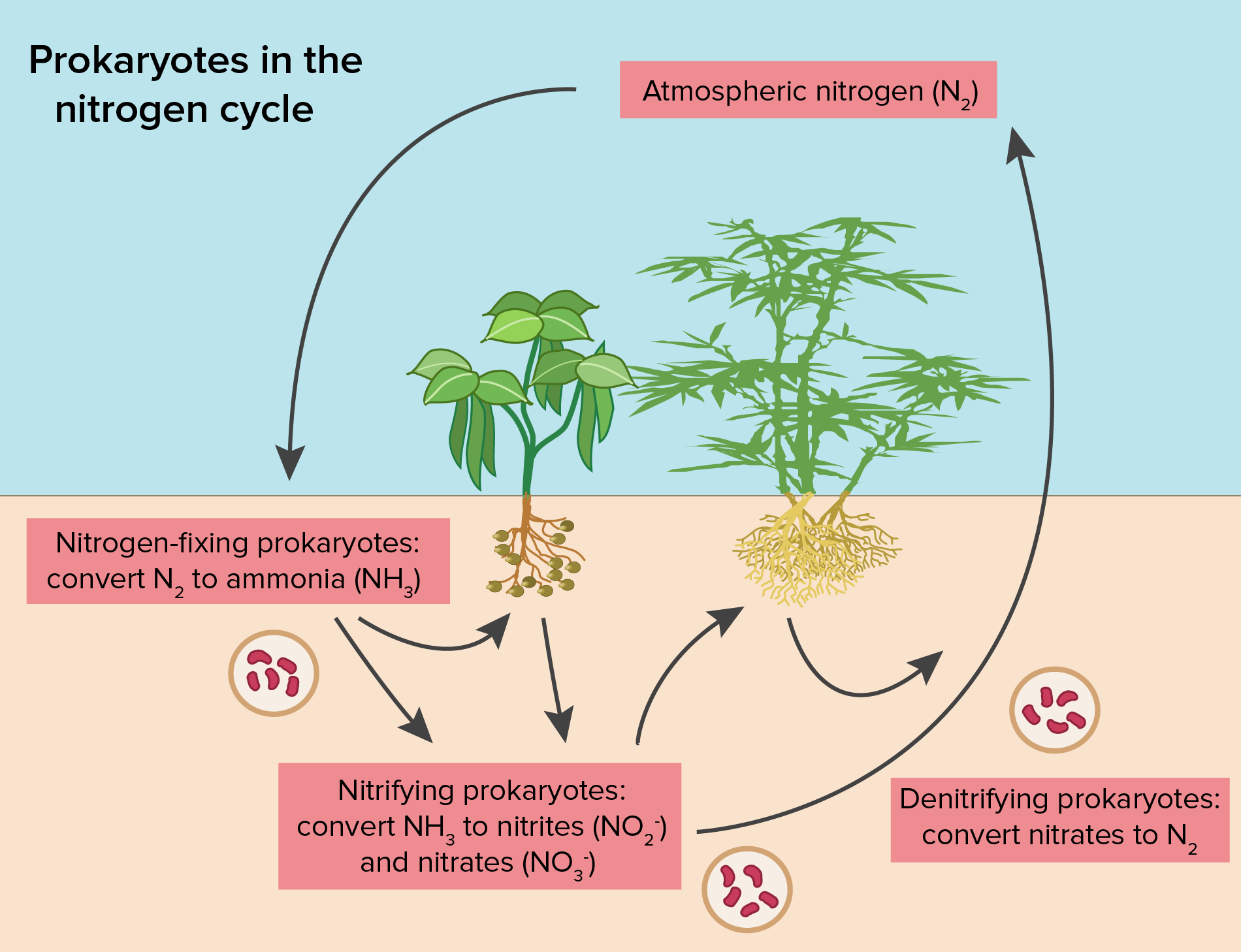
The nitrogen cycle - ScienceDirect The nitrogen cycle has traditionally been divided into three processes — N 2 fixation, nitrification, and denitrification — and microbes have historically been labeled by their identified participation in one of these processes, that is, 'nitrogen fixers', 'nitrifiers' and 'denitrifiers'.This assignment of microbes to specific eco-physiological cohorts based on their ...
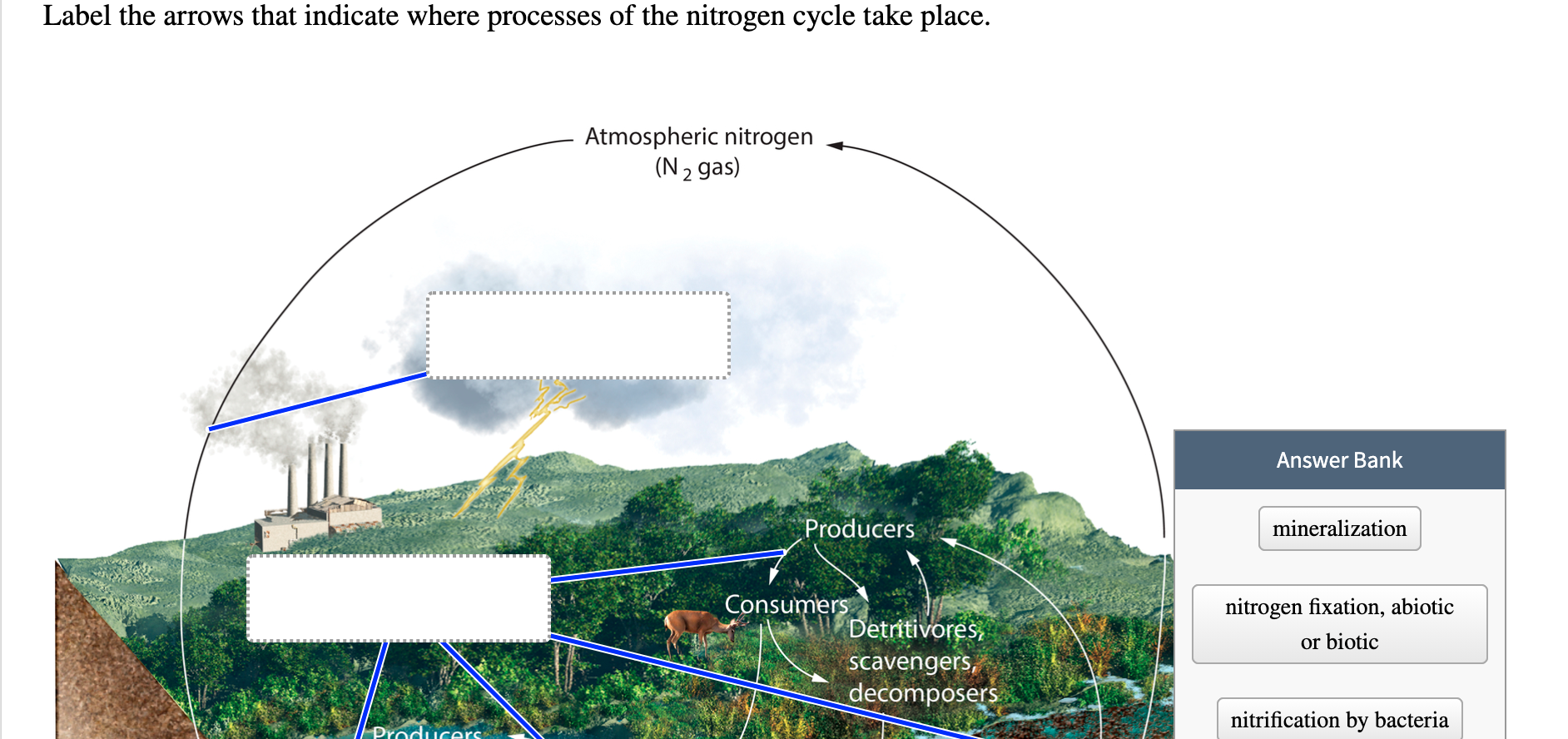
Nitrogen cycle label
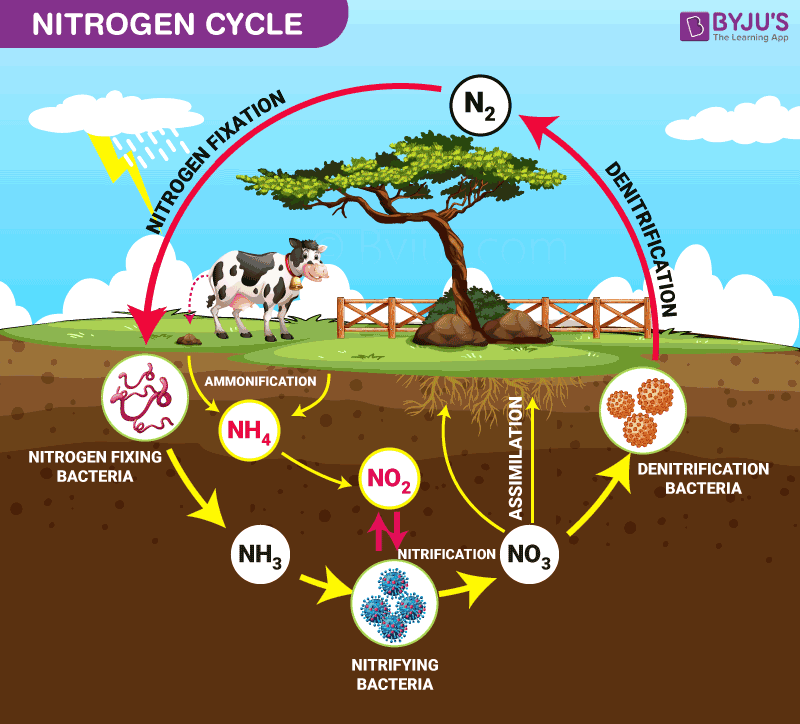
The Nitrogen Cycle and its Processes | Earth Eclipse Processes of the Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting the atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) into biological state nitrogen. It is the first process of making nitrogen available for plants. It is defined as an anaerobic (without oxygen) process that catalyzes the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) into ammonia (NH 3 ). Nitrogen Cycle Explained - Definition, Stages and Importance Nitrogen Cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction. Biogeochemical Cycles | Center for Science Education The element carbon is a part of seawater, the atmosphere, rocks such as limestone and coal, soils, as well as all living things. On our dynamic planet, carbon is able to move from one of these realms to another as a part of the carbon cycle. 1. Carbon moves from the atmosphere to plants. In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to oxygen in a gas call...
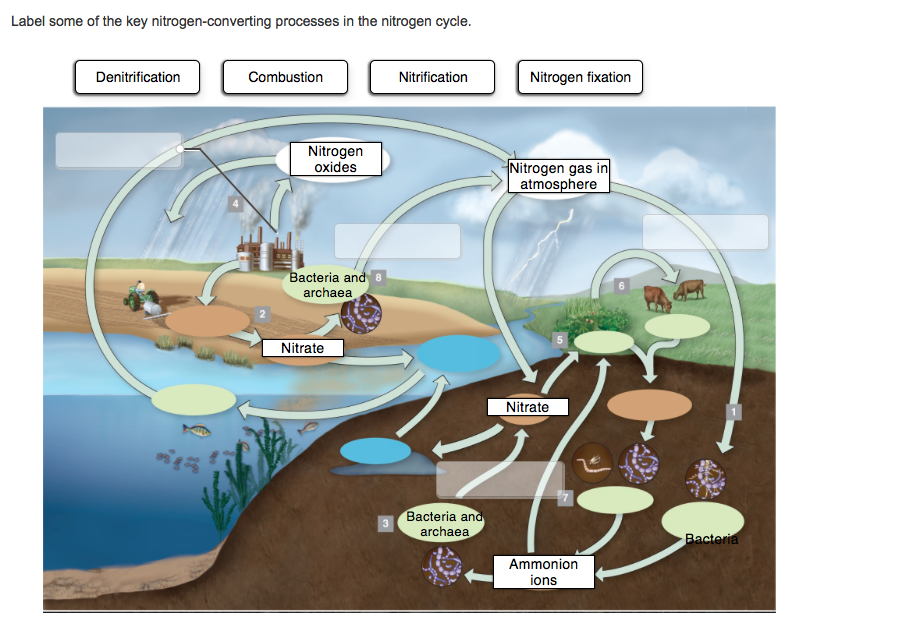
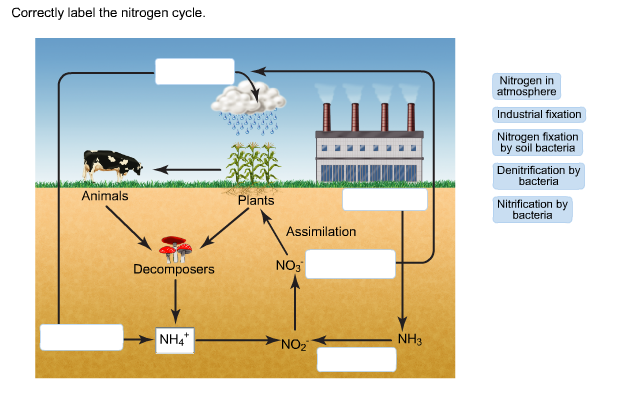
Nitrogen cycle label. Nitrogen cycle | Definition & Steps | Britannica nitrogen cycle, circulation of nitrogen in various forms through nature. Nitrogen, a component of proteins and nucleic acids, is essential to life on Earth. Although 78 percent by volume of the atmosphere is nitrogen gas, this abundant reservoir exists in a form unusable by most organisms. Label the Nitrogen Cycle Diagram | Quizlet Start studying Label the Nitrogen Cycle. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. Scheduled maintenance: Thursday, December 22 from 3PM to 4PM PST hello quizlet Home Subjects Expert solutions Create Study sets, textbooks, questions Log in Sign up Upgrade to remove ads Only $35.99/year Label the Nitrogen Cycle The nitrogen cycle (article) | Ecology | Khan Academy Nitrogen cycling in marine ecosystems So far, we’ve focused on the natural nitrogen cycle as it occurs in terrestrial ecosystems. However, generally similar steps occur in the marine nitrogen cycle. There, the ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification processes are performed by marine bacteria and archaea. Diagram of the Nitrogen Cycle | U.S. Geological Survey Detailed Description This diagram of the nitrogen cycle shows were in the cycle antibiotics could impact the ability of denitrifying bacteria to process nitrates and nitrites in groundwater. The diagram is a modified version of figure 9 from USGS SIR 2004-5144, page 16. This study was funded by the USGS's Toxic Substances Hydrology Program.
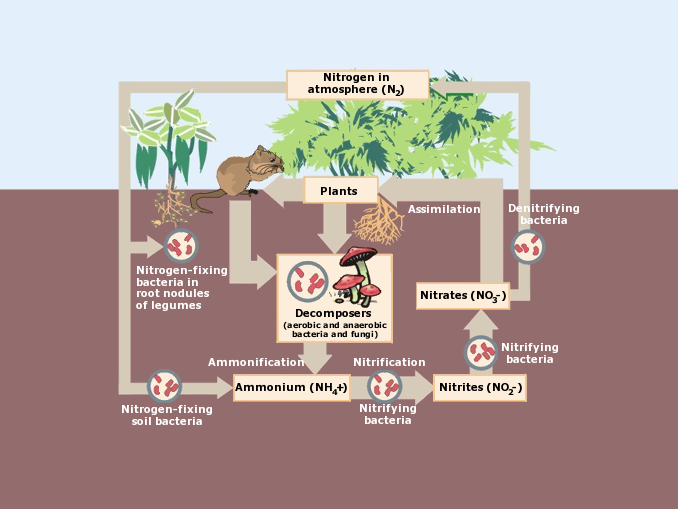
Nitrogen Cycling in Agriculture | Cooperative Extension | University of ... The Nitrogen Cycle Let's begin our discussion of the N cycle in a typical grain crop rotation (corn, wheat, double-crop beans) by considering the plant residue left on the field surface after harvest. Crop residues that are left on the soil surface or incorporated into the topsoil during tillage provide a source of organic matter to the soil. The Nitrogen Cycle Game | My NASA Data The Nitrogen Cycle Share Watch on Review the processes involved with moving nitrogen in the cycle. Fixation: converts nitrogen in the air to ammonium, biologically available Nitrification: bacteria change ammonium to nitrates to be absorbed by plants Assimilation: plants absorb nitrates by the roots With Aid of a labeled diagram, describe the Nitrogen cycle ... Nitrogen is highly abundant in gas form in our atmosphere, making up 78 percent of the total gases. All living organisms must receive nitrogen so that they ... Nitrogen Cycle - Definition, Steps, Importance with Diagram The entire process of the Nitrogen Cycle, one of the important biogeochemical cycle takes place in five stages: 1) Nitrogen Fixation by Bacteria - Converting inert atmospheric nitrogen (N 2 )into biologically available forms such as ammonia (NH 3 ), nitrates, or nitrites. 2) Nitrification by Bacteria - Converting ammonia to nitrite and then ...
Nitrogen cycle - Wikipedia The nitrogen cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which nitrogen is converted into multiple chemical forms as it circulates among atmospheric, terrestrial, and marine ecosystems. The conversion of nitrogen can be carried out through both biological and physical processes. Nitrogen Cycle - Liveworksheets Nitrogen Cycle worksheet Live worksheets > English Nitrogen Cycle Label the nitrogen cycle ID: 1319404 Language: English School subject: Science Grade/level: 7 Age: 9-13 Main content: Science Cycles of matter Other contents: Add to my workbooks (92) Download file pdf Embed in my website or blog Add to Google Classroom Add to Microsoft Teams The nitrogen cycle — Science Learning Hub Nitrogen is a crucially important component for all life. It is an important part of many cells and processes such as amino acids, proteins and even our DNA. It is also needed to make chlorophyll in plants, which is used in photosynthesis to make their food. As part of these life processes, nitrogen is transformed from one chemical form to another. Nitrogen Cycle (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Nitrogen cycle, the micro-organisms mediated cycle, is based on four major chemical transformations. (i) Nitrogen fixation where molecular N 2 is fixed as organic nitrogen by Rhizobium bacteria. (ii) Nitrification is the process of oxidising NH 3 to NO -3 by Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter. (iii) Nitrate reduction to nitrite ion.
Nitrogen Cycle - Definition, Steps and Importance | Biology ... Jan 15, 2021 · The nitrogen cycle refers to the cycle of nitrogen atoms through the living and non-living systems of Earth. The nitrogen cycle is vital for life on Earth. Through the cycle, atmospheric nitrogen is converted to a form which plants can incorporate into new proteins. Nitrogen Cycle Explained
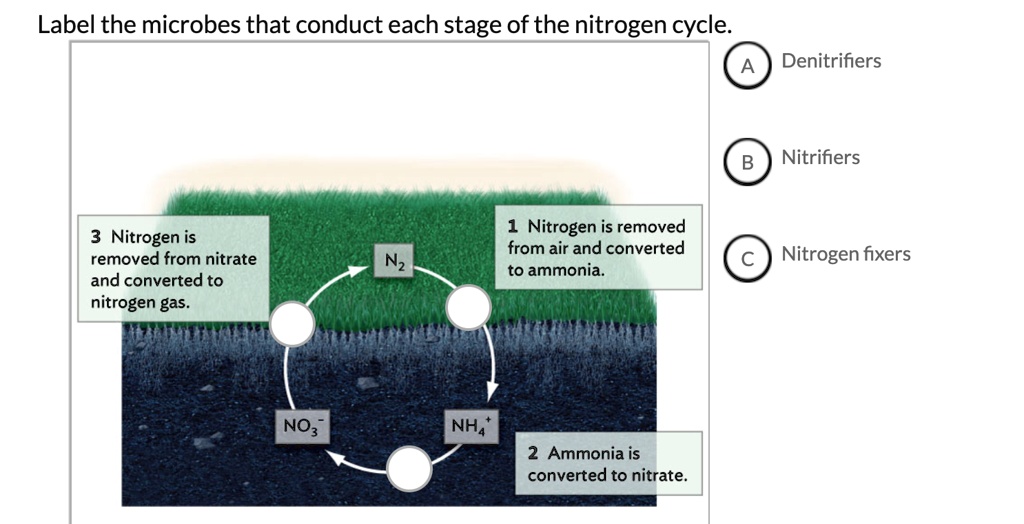
Solved 1. Fill in the box below with the name of a | Chegg.com 1. Fill in the box below with the name of a compartment from either the carbon or the nitrogen cycle. Label the left arrow with a type of transfer which brings the element into this pool, and the right arrow with a process which removes the element from this pool. 2. Choose two different factors that can cause substantial changes in the genetic ...
Nitrogen Cycle | Components, Process, Role, The Cyclic Path Nitrogen is a part of proteins and nucleic acids found in all the living cells. proteins make more than 50% of the dry mass of cells. They are the most abundant organic compounds present in the biosphere and contain nitrogen. Hydrosphere: Nitrates and nitrites present in oceans and seas constitute the nitrogen present in the hydrosphere.
Carbon Cycle, Nitrogen Cycle, Phosphorus and Sulphur Cycle Nitrogen Cycle (Gaseous Cycle) Apart from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen, nitrogen is the most prevalent element in living organisms. Nitrogen is a constituent of amino acids, proteins, hormones, chlorophylls and many of the vitamins (explained in Biology NCERT). Plants compete with microbes for the limited nitrogen that is available in the soil.
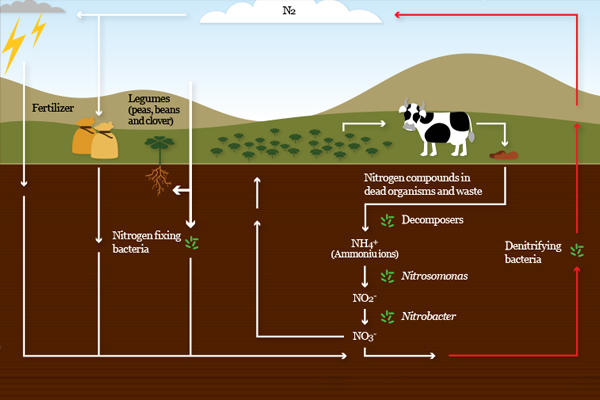
Nitrogen Cycle: Definition, Steps, Importance and Solved Example Answer: The nitrogen cycle is the recycling phase of the nitrogen which includes nitrogen fixation, ammonification, nitrification, and denitrification. Denitrification is the process through which the nitrates and nitrites are converted back to atmospheric nitrogen. This process is performed by the anaerobic bacteria.
Nitrogen Cycle (With Diagram) | Ecology - Zoology Notes Once in the biological realm, the first step in the nitrogen cycle is ammonification—a process that involves the hydrolysis of protein and oxidation of amino acids, resulting in the production of ammonia (NH 3 ). This transformation is carried out by all organisms, where during the initial breakdown of amino acids, energy is released (Table ...
Understanding Nitrogen Cycle with a Diagram - Biology Wise Also known as ammonification, the organic form of nitrogen from the animal wastes, dead and decayed living organisms is converted into inorganic form. In this nitrogen cycle step, decomposers (bacteria and fungi) act on the decayed organic matter containing nitrogen and convert it into ammonium (NH4+). Nitrification
Nitrogen Cycle | U.S. Geological Survey Detailed Description. Figure 1. Nitrogen cycles continuously between the atmosphere, soil, and organisms. Nitrogen in the atmosphere and nitrogenous compounds in the soil are converted into substances that can be used by plants before being returned to the air and soil.
NITROGEN CYCLE LESSON PLAN - Kesler Science The nitrogen cycle lesson includes a PowerPoint with activities scattered throughout to keep the students engaged. The students will also be interacting with their journals while taking notes from the PowerPoint. If you have students that need modified notes, the 5E lessons come equipped to help give every student access to the lesson.
Nitrogen Cycle - Process, Steps (with Diagrams) - Explained Image 2: Nitrogen fixation is the first phase of the nitrogen cycle. Picture Source: wikimedia.org Fixation - The nitrogen in the atmosphere is in the inert form and only a few organisms can benefit from it. For it to be useful to all life forms, it should be converted to fixed or organic form. Hence, the process is called nitrogen fixation.
5 Stages of Nitrogen Cycle (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion Nitrogen being 79 per cent of the atmosphere, the atmospheric phase is predominant in the global nitrogen cycle. It is required by organisms in the synthesis of proteins, nucleic acids, and other nitrogenous compounds. Atmospheric nitrogen serves as the ultimate source.
Nitrogen Cycle Diagram | Quizlet This is part of the decaying process. When a plant or animal dies, decomposers like fungi and bacteria turn the nitrogen inside of the cells back in ammonium ions (NH4+) so it can reenter the nitrogen cycle. Nitrate (NO3-) in the soil gets converted to Nitrogen gas (N2) by specific bacteria and then float back out into the atmosphere.
Biogeochemical Cycles | Center for Science Education The element carbon is a part of seawater, the atmosphere, rocks such as limestone and coal, soils, as well as all living things. On our dynamic planet, carbon is able to move from one of these realms to another as a part of the carbon cycle. 1. Carbon moves from the atmosphere to plants. In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to oxygen in a gas call...
Nitrogen Cycle Explained - Definition, Stages and Importance Nitrogen Cycle is a biogeochemical process through which nitrogen is converted into many forms, consecutively passing from the atmosphere to the soil to organism and back into the atmosphere. It involves several processes such as nitrogen fixation, nitrification, denitrification, decay and putrefaction.
The Nitrogen Cycle and its Processes | Earth Eclipse Processes of the Nitrogen Cycle. Nitrogen fixation is the process of converting the atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) into biological state nitrogen. It is the first process of making nitrogen available for plants. It is defined as an anaerobic (without oxygen) process that catalyzes the reduction of atmospheric nitrogen (N 2) into ammonia (NH 3 ).







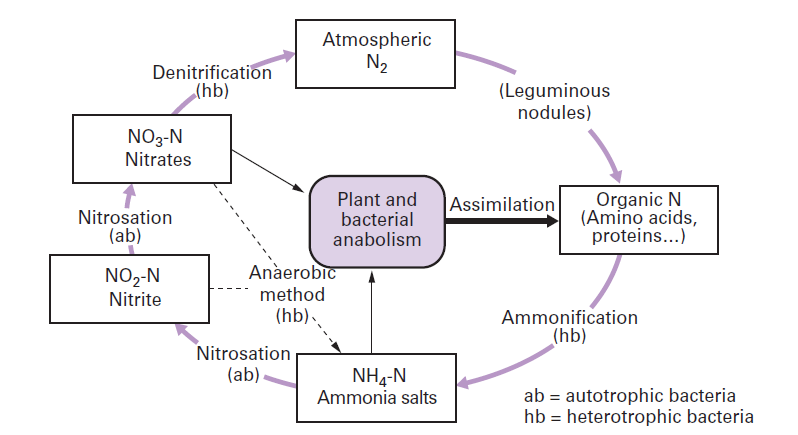


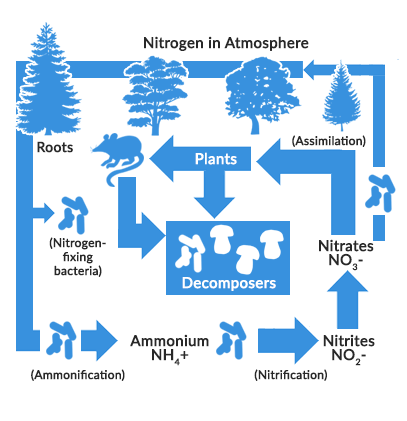
















Post a Comment for "43 nitrogen cycle label"